The table below shows all the basic computer terms and their definitions and images.
Computer Glossary
| TERM |
CLASS DEFINITION |
ALTERNATE DEFINITION |
PICTURE |
| Application Software |
A program which allows us to apply ourselves to a particular page such as editing our image, accessing Internet resources, or playing a game. |
Application software also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with documents. Apps may be bundled with the computer and its system software, or may be published separately.
|  Google Chrome as application software example Google Chrome as application software example |
| ASCII |
American Standard Code for Information Interchanged. An international Standard for encoding charecters into 7 bit codes. ASCII is the basis of the more modern and inclusive Unicode standard. |
ASCII is an acronym for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. ASCII is a code for representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127. Most computers use ASCII codes to represent text, which makes it possible to transfer data from one computer to another.The standard ASCII character set uses just 7 bits for each character. |
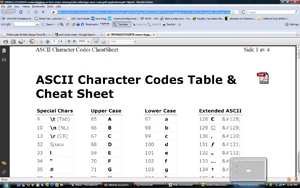 ASCII code chart ASCII code chart |
| Binary Code |
A scheme for encoding data using only the digits 0 and 1.Binary Code can be used to encode text images, sounds and programs amongst other data. |
Computers are based on the binary numbering system, which consists of just two unique numbers, 0 and 1. All operations that are possible in the decimal system (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) are equally possible in the binary system. |
 Binary Code Binary Code |
| Bit |
Contraction of the term binary digit, hence 0 or 1. |
Bit Short for binary digit, the smallest unit of information on a machine. The A single bit can hold only one of two values: 0 or 1. More meaningful information is obtained by combining consecutive bits into larger units. For example, a byte is composed of 8 consecutive bits. |
 The two binary digits The two binary digits |
| Booting |
The process by which a computer loads its operating system in primary storage from secondary storage using the the instructions found in ROM. |
Booting is loading the first piece of software that starts a computer. Because the operating system is essential for running all other programs, it is usually the first piece of software loaded during the boot process. |
 Windows booting image Windows booting image |
| Bus |
An electrical connection through which data are transmitted. It has a sending and receiving station. |
Bus is an electrical pathway through which the processor communicates with the internal and external devices attached to the computer. Bus transfers the data between the computer subsystems and between the computers and sends the instructions and commands to and from the processor the different devices. It connects all internal computer components to the main memory and the central processing unit (CPU). |
 Computer Bus Computer Bus |
| Byte |
Contraction of the term binary term, the smallest unit of information which can be accessed directly by a computer.Most modern computers use 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, 64-bit. |
Byte is a sequence of adjacent bits, usually eight, operated on as a unit by a computer. |
 Series of bytes Series of bytes |
| Charecter |
a single letter or digit, or a special sympbol, like a punctuation mark, the dollar sign, and a blank space. |
Charecter in a computer software, is any symbol that requires one byte of storage. This includes all the ASCII and extended ASCII characters, including the space character. |
 Alphabet letters and symbols Alphabet letters and symbols |
| Computer |
a programmable electronic device for the processing of information. |
Computer is defined as a programmable machine that responds to a specific set of instructions in a well-defined manner, and it can execute a prerecorded list of instructions (or a program). |
 Computer Computer |
| CPU |
Central Processing Unit; a miniaturized electronic component which controls the execution of a computer and which performs basic arithmetic and logical operations.Colloquially, it's called the computer's "brain". |
The central processing unit CPU is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. |
 CPU with open case CPU with open case |
| Directory |
A logical collection of files stored under a single name. |
Directory is an organizational unit, or container, used to organize folders and files into a hierarchical structure.The files and directories at any level are contained in the directory above them. |
 Window showing computer directory Window showing computer directory |
| File |
A logical collection of data stored under a single name. |
File is a collection of data stored in one unit, identified by a filename. It can be a document, picture, audio or video stream, data library, application, or other collection of data. |
 Window showing files Window showing files |
| Firewire |
Apple's name for the 1EEE 1394 highspeed serial bus. Also called i Link by Sony, and Linux by Texas Instruments; it can be different sizes. |
Firewire is a high-speed interface for connecting peripherals. Created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, Firewire can be used to connect devices such as digital video cameras, hard drives, audio interfaces, and MP3 players, such as the Apple iPod, to your computer.You may see Firewire referred to by its technical name, IEEE 1394, since it was standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. |
 1EEE 1394 image 1EEE 1394 image |
| Gigabyte |
Two to the power thirty bytes (approx. a billion bytes) |
Gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power (1,073,741,824) bytes. Gigabyte is often abbreviated as G or GB. |
 Gigabyte motherboard Gigabyte motherboard |
| Hardware |
The physical parts of the computer, any part of the computer which can be seen and touched. |
Hardware refers to objects that you can actually touch, like disks, disk drives, display screens, keyboards, printers, boards, and chips. In contrast, software is untouchable. Software exists as ideas, concepts, and symbols, but it has no substance. |
 Physical parts of a computer Physical parts of a computer |
| Information |
Words, pictures, and sounds which can have meaning to us. |
Information is stimuli that has meaning in some context for its receiver. When information is entered into and stored in a computer, it is generally referred to as data. After processing (such as formatting and printing), output data can again be perceived as information. |
 Blue person carrying heap of information Blue person carrying heap of information |
| Input Devices |
Devices used to put information into a computer. Common examples of input devices are keyboards, mouses and scanners. |
Input Device is any device that provides input to a computer. There are dozens of possible input devices, but the two most common ones are a keyboard and mouse. |
 Examples of input devices Examples of input devices |
| Kilobyte |
2¹º (approx. thousand bytes) |
Kilobyte is approximately a thousand bytes (actually, 2 to the 10th power, or decimal 1,024 bytes). |
|
| Megabyte |
2²º(approx. million bytes) |
Megabyte (abbreviated MB) is 2 to the 20th power bytes, or 1,048,576 bytes in decimal notation. |
|
| Monitor |
A visual-display device on which a computer displays information about its internal state, allowing people to monitor the activities of the computer. |
Monitor is often used synonymously with "computer screen" or "display." The monitor displays the computer's user interface and open programs, allowing the user to interact with the computer. |
 Computer monitor Computer monitor |
| Operating System |
A set of programs which tells a computer how to perform its most basic task, such as "reading" information from input devices, "writing" information to output devices, and executing the instructions of launched software. |
Operating System is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. |
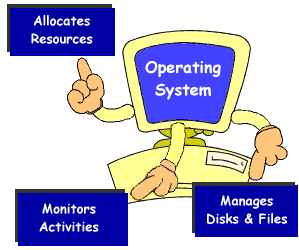 Functions of Operating Systems Functions of Operating Systems |
| Output Devices |
Devices used by a computer used to put out information. Common examples of output devices are monitors, printers, LED lights, etc. |
Output Devices is any device that outputs information from a computer is called, not surprisingly, an output device. Since most information from a computer is output in either a visual or auditory format, the most common output devices are the monitor and speakers. These two devices provide instant feedback to the user's input, such as displaying characters as they are typed or playing a song selected from a playlist. |
 Examples of output devices Examples of output devices |
| Peripheral |
Any hardware element that is peripheral to a computer's system unit. Common examples are input and output devices. Even output devices which are found within the system unit are considered peripherals because they are peripheral to the computer. |
Peripheral is any external device that provides input and output for the computer. For example, a keyboard and mouse are input peripherals, while a monitor and printer are output peripherals. Computer peripherals, or peripheral devices, are sometimes called "I/O devices" because they provide input and output for the computer. Some peripherals, such as external hard drives, provide both input and output for the computer. |
 Peripheral Devices Peripheral Devices |
| Primary Storage |
A miniaturized electronic component, which provides temporary storage of information. Primary Storage is volatile and relatively expensive(depends on supply of electricity), but it's used because it is fast and is the only storage that the CPU can access. |
Primary Storage (or main memory or internal memory), often referred to simply as memory, is the only one directly accessible to the CPU. The CPU continuously reads instructions stored there and executes them as required. Any data actively operated on is also stored there in uniform manner. |
 Primary Storage Devices Primary Storage Devices |
| Programmable |
Capable of performing variable and different tasks, limited only by the sophistication of the program provided. |
Programmable :an electronic device, as a calculator or telephone, that can be programmed to perform specific tasks. |
 Microwave Oven Microwave Oven |
| Program |
A set of instructions which tell a computer what to do and when to do it; the instructions must be written in a language the computer understands. |
Program is a set of instructions for a computer to perform a specific task. Programs generally fall into these categories applications, utilities or services. |
 different programs different programs |
| RAM |
Random Access Memory; we can access it in random order. |
RAM acronym for random access memory, a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly; that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes. RAM is the most common type of memory found in computers and other devices, such as printers. |
 Computer Ram Computer Ram |
| ROM |
Read Only Memory; continous just enough information for the computer to read first bit of operating system, which tells the second bit what to do next. |
ROM stands for "Read-Only Memory." ROM is memory containing hardwired instructions that the computer uses when it boots up, before the system software loads. |
 ROM chip ROM chip |
| Root |
Short for root directory, it's the main directory in a hierarchical directory structure which logically contains all other directories; in DOS and Windows-based systems, the root directory is represented by a backslash(\), in Mac OS, Unix, and Linux systems, the root directory is represented with a slash (/). |
Root refers to the top-level directory of a file system. The word is derived from a tree root, since it represents the starting point of a hierarchical tree structure. |
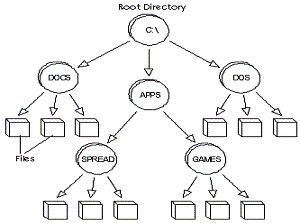 Root Directory Root Directory |
| Secondary Storage |
Any storage medium which provides relatively permanent storage of information. Secondary storage is non-volatile and relatively inexpensive, with few exceptions, secondary storage can not be accessed directly by the CPU. The most common examples are magnetic and optical discs, magnetic tapes, and flash memory. |
Secondary Storage is any non-volatile storage medium that is not directly accessible to the processor. he CPU like main memory ("memory mapped"). Reading and writing these registers can cause the device to perform actions like reading a block of data off a disk or rewinding a tape. Programs and data stored in secondary storage must first be loaded into main memory before the processor can use them. |
 Optical Disk Optical Disk |
| Software |
Synonym for program. |
Software is a general term that describes computer programs. Related terms such as software programs, applications, scripts, and instruction sets all fall under the category of computer software. |
 Microsoft Ofiice Home Student" Microsoft Ofiice Home Student" |
| String |
a connection of like units, treated as a whole, examples character string and bit string. |
String is a data type used in programming, such as an integer and floating point unit, but is used to represent text rather than numbers. It is comprised of a set of characters that can also contain spaces and numbers. |
 example of a character string example of a character string |
| System Unit |
A plastic or metal box which contains the principal parts of a computer. The CPU, RAM, ROM, various connection cables, and an AC/DC converter. In modern micro-computers, it's common to find peripheral devices installed inside the system unit. Examples include modem and card reader. |
System Unit is the technical term that refers to the box that houses your computer. The system unit refers to the computer itself but does not include the monitor, the keyboard, the mouse, or any other peripherals. I suppose most people will probably know what you mean when you refer to "the box," but saying "system unit" will definitely make you sound more sophisticated. |
 System Unit System Unit |
| USB |
Univeral Serial Bus; a standard for correcting peripherals to a computer over inexpensive cables. |
USB is a standardized serial computer interface that allows simplified attachment of peripherals. |
 USB stick USB stick |
© Copyright 2011 Pooja Kesh. All rights reserved.
All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners.
 Google Chrome as application software example
Google Chrome as application software example ASCII code chart
ASCII code chart Binary Code
Binary Code The two binary digits
The two binary digits Windows booting image
Windows booting image Computer Bus
Computer Bus Series of bytes
Series of bytes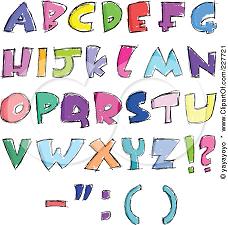 Alphabet letters and symbols
Alphabet letters and symbols Computer
Computer CPU with open case
CPU with open case Window showing computer directory
Window showing computer directory Window showing files
Window showing files 1EEE 1394 image
1EEE 1394 image Physical parts of a computer
Physical parts of a computer Blue person carrying heap of information
Blue person carrying heap of information Examples of input devices
Examples of input devices Computer monitor
Computer monitor Functions of Operating Systems
Functions of Operating Systems Examples of output devices
Examples of output devices Peripheral Devices
Peripheral Devices Primary Storage Devices
Primary Storage Devices Microwave Oven
Microwave Oven different programs
different programs Computer Ram
Computer Ram ROM chip
ROM chip Root Directory
Root Directory Optical Disk
Optical Disk Microsoft Ofiice Home Student"
Microsoft Ofiice Home Student" example of a character string
example of a character string System Unit
System Unit USB stick
USB stick