| Term |
Image |
Description |
Resource description |
| Application Software |

An example of some Application Software icons(ref.35). |
A program which allows us to apply ourselves to a particular task, such as editing an image, accessing internet resources, or playing a game. |
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks(ref.1). |
ASCII |
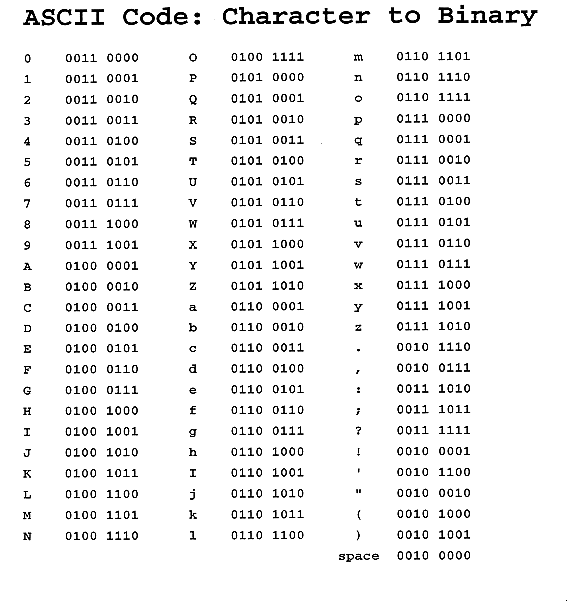
ASCII Code: Character to Binary(ref.36). |
"American Standard Code" for information interchange, an international standard for encoding characters into 7-bit code; ASCII is the basics of the more modern and inclusive Unicode statement. |
A standard code, consisting of 128 7-bit combinations, for characters stored in a computer or to be transmitted between computers(ref.2). |
Binary Code |

An example of Binary Code(ref.37). |
A scheme for encoding data using only the digits 0 and 1; Binary code can be used to encode text,images ,sounds, and programs, amongst the data. |
A binary code is a way of representing text or computer processor instructions by the use of the binary number system's two-binary digits 0 and 1. This is accomplished by assigning a bit string to each particular symbol or instruction. For example, a binary string of eight binary digits (bits) can represent any of 256 possible values and can therefore correspond to a variety of different symbols, letters or instructions(ref.3). |
Bit |

One of these Binary Codes is a Bit(ref.38). |
Contraction of the term binary digit, hence 0 or 1. |
A bit (a contraction of binary digit) is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system(ref.4). |
Booting |

Booting process(the computer is turning on)(ref.39). |
Short for "Boot Strapping". The process by which a computer loads it's operating system in primary storage from secondary storage using the instructions found in ROM. |
In computing, booting (also known as booting up) is a process that begins when a user turns on a computer system and prepares the computer to perform its normal operations. On modern computers, this typically involves loading and starting an operating system(ref.5). |
Bus |

An example of a Bus in the C.P.U(ref.40). |
An electrical connection through which data are transmitted. |
In computer architecture, a bus is a subsystem that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers.Early computer buses were literally parallel electrical wires with multiple connections, but the term is now used for any physical arrangement that provides the same logical functionality as a parallel electrical bus. Modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit serial connections(ref.6). |
Byte |

Showing a Byte(ref.41). |
Contraction of the term binary term, the smallest unit of information which can be accessed directly by a computer. Most modern computers use 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit or 64-bit bytes. |
A sequence of adjacent bits, usually eight, operated on as a unit by a computer(ref.7). |
Character |

Represents different Characters(ref.42). |
A single letter or digit, or a special symbol like punctuation marks, the dollar sign and a blank space. |
A character is any letter, number, space, punctuation mark, or symbol that can be typed on a computer. The word "computer," for example, consists of eight characters(ref.8). |
Computer |

An example of a Computer(ref.43). |
An electronic device that as a system performs many desired tasks for a user.A programmable electronic device for the processing of information. |
Also called processor. an electronic device designed to accept data, perform prescribed mathematical and logical operations at high speed, and display the results of these operations(ref.9). |
CPU |

The Central Processing Unit of a Computer(ref.44). |
"Central Processing Unit", a miniaturized electronic component which controls the exception of a computer and which performs basic arithemetic and logical operations. Collaquially called the computer's "Brain". |
"Central processing unit": the key component of a computer system, which contains the circuitry necessary to interpret and execute program instructions(ref.10). |
Directory |

Directory that stores a collection of files(ref.45). |
A logical collection of files stored under a single name. |
A folder directory, in which groups of computer files and other folders can be kept and organized.A typical file system may contain thousands (or even hundreds of thousands) of folders. Files are kept organized by storing related files in the same folder. The folder can also be referred to as the root. A folder contained inside another folder is called a subfolder, subdirectory, or child of that folder(ref.11). |
File |

A file that contains word,images etc(ref.46). |
A logical collection of data stored under a single name. |
A collection of data or information that has a name, called the filename. Almost all information stored in a computer must be in a file. There are many different types of files: data files, text files , program files, directory files, and so on. Different types of files store different types of information(ref.12). |
Firewire |

An "IEEE" 1394 Firewire(ref.47). |
Apple's name for the "IEEE" 1394, high speed serial bus, also called i LINK by Sony and Lynx by Texas Instruments. |
Created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, Firewire can be used to connect devices such as digital video cameras, hard drives, audio interfaces, and MP3 players, such as the Apple iPod, to your computer. A standard Firewire connection can transfer data at 400 Mbps, which is roughly 30 times faster than USB(ref.13). |
Gigabyte |

Gigabyte Motherboard(ref.48). |
2 to the power of 30 bytes(approximately 1 billion bytes). |
A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity equal to 1,024 megabytes (2 to the power of 30 bytes/ One billion bytes)(ref.14). |
Hardware |

Examples of Hardware Devices(ref.49). |
The physical parts of the computer, any part of the computer which can be seen and touched. |
Computer hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer and related devices. Internal hardware devices include motherboards, hard drives, and RAM. External hardware devices include monitors, keyboards, mice, printers, and scanners.The internal hardware parts of a computer are often referred to as components, while external hardware devices are usually called peripherals. Together, they all fall under the category of computer hardware(ref.15). |
Information |

A Word Document(ref.50). |
Word,pictures and sounds which have meaning to us, (if they don't have meaning then it is not information to us). |
Information is the summarization of data. Technically, data are raw facts and figures that are processed into information, such as summaries and totals(ref.16). |
Input Devices |

Examples of Input Devices(ref.51). |
Devices used to put information into a computer.Common examples of input devices are:
- keyboards
- mouses
- scanners
- microphones
- cameras
- gyroscopes
- game controllers
- USB drives
- infrared remote controls
- touch pads
- touch screens
- graphic tablets
- disc drives
- flash memory cards
- motion sensors
- modem
|
Input devices are things we use to put information INTO a computer(ref.17). |
Kilobyte |

Kilobyte chart(ref.52). |
2 to the power of 10 bytes(approximately 1 thousand bytes). |
A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity equal to 1,024 (2 to the power of 10 bytes/One thousand bytes)(ref.18). |
Megabyte |

Types of Bytes(ref.53). |
2 to the power of 20 bytes(approximately 1 million bytes). |
A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity equal to 1,048,576 (2 to the power of 20 bytes/One million bytes)(ref.19). |
Monitor |

Monitor(ref.54). |
A visual-display device, on which a computer displays information about it's internal state, allowing people to monitor the activities o fthe computer. |
The term "monitor" is often used synonymously with "computer screen" or "display." The monitor displays the computer's user interface and open programs, allowing the user to interact with the computer, typically using the keyboard and mouse(ref.20). |
Operating System |

"Apple" is an operating system(ref.55). |
A set of programs which tells a computer hot to perform it's most basic tasks, such as "reading" information from input devices, "writing" information to output devices, and executing the instructions of launched software. |
The most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers(ref.21). |
Output Devices |

Examples of output Devices(ref.56). |
Devices used by a computer to put out information.Common examples of output devices are:
- monitors
- printers
- speakers
- headphones
- data projectors
- fax modem
- data modem
- LED lights
- game controllers(some)
- disk drive
- USB key
- and all secondary storage devices
|
Any device that outputs information from a computer is called, an output device. Since most information from a computer is output in either a visual or auditory format, the most common output devices are the monitor and speakers(ref.22). |
Peripheral |

Examples of Peripherals(ref.57). |
Any hardware element which is peripheral to a computer's system unit. Common examples are input devices and output devices. Even output devices which are often found within the system unit. |
Electronic equipment connected by cable to the CPU of a computer(ref.23). |
Primary Storage |

Primary Storage electronic component(ref.58). |
A miniaturized electronic component which provides temporary storage of information.Primary storage is volatile and relatively expensive, but it is used because it's fast and (with few exceptions) is the only storage which the CPU can acess directly. |
Primary storage, also known as main storage or memory, is the main area in a computer in which data is stored for quick access by the computer's processor. On today's smaller computers, especially personal computers and workstations, the term random access memory (RAM) - or just memory is used instead of primary or main storage(ref.24). |
Programmable |

A watch is programmable(ref.59). |
Capable of performing varied and different tasks, limited only be the sophistication of the progarms provided. |
Capable of being programmed for automatic operation or computer processing(ref.25). |
Program |

A program is written in a language a computer can understand(ref.60). |
A set of instructions which tells a computer what to do and when to do it, the instructions must be written in a language that the computer understands. |
A computer program (also software, or just a program) is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task with a computer. A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor.The program has an executable form that the computer can use directly to execute the instructions(ref.26). |
RAM |

RAM memory card(ref.61). |
It's called "Random Access Memory" because we can access it in random order. |
Short for "Random Access Memory", a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly; that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes. RAM is the most common type of memory found in computers and other devices, such as printers(ref.27). |
ROM |

ROM memory card(ref.62). |
"Read Only Memory" is computer memory that can permanently store data and applications within it. . |
Short for "Read-only Memory", computer memory on which data has been prerecorded. Once data has been written onto a ROM chip, it cannot be removed and can only be read.Unlike main memory (RAM), ROM retains its contents even when the computer is turned off. ROM is referred to as being nonvolatile, whereas RAM is volatile(ref.28). |
Root |

Root of tree(directories)(ref.63). |
Short for "Root Directory"; the main directory in a hierarchical directory structure, which (logically) contains all other directories; in DOS and Windows based systems, the root directory is represented by a backslash (\) in Mac OS, Unix, and linux systems, the root directory is represented by a slash (/). |
The top directory in a file system. The root directory is provided by the operating system and has a special name; for example, in DOS systems the root directory is called \. The root directory is sometimes referred to simply as the root(ref.29). |
Secondary Storage |

Secondary Storage Block(ref.64). |
Any storage medium which provides (realtively) permanent storage of information. Secondary storage is non-volatile and relatively inexpensive, but it's slow. With few exceptions, secondary storage cannot be accessed directly by the CPU. |
Secondary storage, sometimes called auxiliary storage, is all data storage that is not currently in a computer's primary storage or memory. An additional synonym is external storage(ref.30). |
Software |

Software icons(ref.65). |
A synonym of program. |
Computer instructions or data. Anything that can be stored electronically is software. The storage devices and display devices are hardware(ref.31). |
String |

The part put "Home Sweet Home" is a character string(ref.66). |
A collection of like units, treated as a whole, example: Character string and Bit string. |
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable(ref.32). |
System Unit |

System Unit(ref.67). |
A plastic or metal box which contains the principal parts of a computer. |
The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard or monitor, or any peripheral devices(ref.33). |
USB |

USB(ref.68). |
"Universal Serial Bus", a standard for connecting peripherals to a computer over inexpensive cables. |
"Universal Serial Bus", the most widely used hardware interface for attaching peripherals to a computer(ref.34). |
































