





























| Term | Touque.ca definition | Alternate Definition | Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application software | (ref. 1 ) A program which allows us to apply ourselves to a particular task, such as editing an image, accessing Internet resources, or playing a game. | (ref. 2) A software program that runs on your computer. Web browsers, e-mail programs, word processors, games, and utilities are all applications. The word "application" is used because each program has a specific application for the user. | (photoref. 1 ) |
| ASCII | (ref. 3) American Standard Code for Information Interchange; an international standard for encoding characters into 7-bit codes. ASCII is the basis of the more modern Unicode standard. | (ref. 4) Stands for "American Standard Code for Information Interchange." ASCII is the universal standard for the numerical codes computers use to represent all upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and puctuation. | (photoref. 2 ) |
| Binary code | (ref. 5) Scheme for encoding data which uses only the digits 0 and 1. Binary code can be used to encode text, images, sounds, and programs, amongst other data. | (ref. 6) A two-digit (Base-2) numerical system, which computers use to store data and compute functions. The reason computers use the binary system is because digital switches inside the computer can only be set to either on or off, which are represented by a 1 or 0. | (photoref. 3 ) |
| Bit | (ref. 7) Contraction of the term "BInary diT"; hence, either 0 or 1. | (ref. 8) The computer term "bit" comes from the phrase "Binary DigIT," A bit is a single digit number in base-2 (a zero or a one) and is the smallest unit of computer data. A full page of text is composed of about 16,000 bits. | (photoref. 4 ) |
| Booting | (ref. 9) The process by which a computer loads its operating system into primary storage, from secondary storage, using the instructions found in ROM. | (ref. 10) In simple terms, to boot a computer is to turn it on. Once the computer's power is turned on, the "boot process" takes place. | (photoref. 5 ) |
| Bus | (ref. 11) An electrical connection through which data are transmitted | (ref. 12) Each bus inside a computer consists of set of wires that allow data to be passed back and forth. Most computers have several buses that transmit data to different parts of the machine. Each bus has a certain size, measured in bits (such as 32-bit or 64-bit). Buses also have a certain speed. | (photoref. 6 ) |
| Byte | (ref. 13) Contraction of the term "BinarY TErm"; the smallest unit of information which can be accessed directly by a computer. Most modern microcomputers use 8-bit, 16-bit, or 32-bit bytes. | (ref. 14) A unit of measurement used to measure data. One byte contains eight binary bits, or a series of eight zeros and ones. Therefore, each byte can be used to represent 2^8 or 256 different values. | (photoref. 7 ) |
| Character | (ref. 15) A single letter or digit, or a special symbol like punctuation marks examples are the dollar sign, and a blank space. | (ref. 16) A character is any letter, number, space, punctuation mark, or symbol that can be typed on a computer. The word "computer," for example, consists of eight characters. | (photoref. 8)  |
| Computer | (ref. 17) Programmable electronic device for the processing of information. | (ref. 18) ...a computer is a programmable machine. This means it can execute a programmed list of instructions and respond to new instructions that it is given. | (photoref. 9)  |
| CPU | (ref. 19) Central Processing Unit; a miniaturized electronic component which controls the execution of a computer and which performs basic arithmetic and logical operations. Colloquially called the computer's "brain". | (ref. 20) Stands for "Central Processing Unit." This is the pretty much the brain of your computer. It processes everything from basic instructions to complex functions. Any time something needs to be computed, it gets sent to the CPU. | (photoref. 10 ) |
| Directory | (ref. 21) A logical collection of files, stored under a single name. | (ref. 22) A directory is another name for a folder. Files on your hard disk are organized into various folders, or directories, so that it is easier to keep track of them. | (photoref. 11 ) |
| File | (ref. 23) logical collection of information, stored under a single name. | (ref. 24) A file is a collection of data stored in one unit, identified by a filename. It can be a document, picture, audio or video stream, data library,application, or other collection of data. The following is a brief description of each file type. | (photoref. 12 ) |
| Firewire | (ref. 25) Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus; also called i.LINK by Sony and Lynx by Texas Instruments | (ref. 26) This high-speed interface has become a hot new standard for connecting peripherals. Created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, Firewire can be used to connect devices such as digital video cameras, hard drives, audio interfaces, and MP3 players, such as the Apple iPod, to your computer. | (photoref. 13 ) |
| Gigabyte | (ref. 27) 230 bytes; approximately 1 billion bytes. | (ref. 28) A gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power, or 1,073,741,824 bytes. | (photoref. 14 ) |
| Hardware | (ref. 29) The physical parts of the computer; any part of the computer which can be seen and touched. (cf. software.) | (ref. 30) Computer hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer and related devices. Internal hardware devices include motherboards, hard drives, and RAM. External hardware devices include monitors, keyboards, mice, printers, and scanners. | (photoref. 15 ) |
| Information | (ref. 31) Words, pictures, and sounds which have meaning to us. | ((ref. 32)Knowledge communicated or received concerning a particular fact or circumstance; news | (photoref. 16 ) |
| Input devices | (ref. 33) Devices used to put information into a computer. Common examples of input devices are keyboards, mouses, disc drives, and modems. (See, also,output devices.) | (ref. 34) An input device is any device that provides input to a computer. There are dozens of possible input devices, but the two most common ones are a keyboard and mouse. | (photoref. 17 |
| Kilobyte | (ref. 35) 210 bytes; approximately 1 thousand bytes. | (ref. 36) A kilobyte is 2 to the 10th power, or 1,024 bytes. | (photoref. 18 ) |
| Megabyte | (ref. 37) 220 bytes; approximately 1 million bytes | (ref. 38) A megabyte is 2 to the 20th power, or 1,048,576 bytes. | (photoref. 19 ) |
| Monitor | (ref. 39) A visual-display device, on which a computer displays information about its internal state, allowing people to monitor the activities of the computer. | (ref. 40) The term "monitor" is often used synonymously with "computer screen" or "display." The monitor displays the computer's user interface and open programs, allowing the user to interact with the computer, typically using the keyboard and mouse. | (photoref. 20 ) |
| Operating system | (ref. 41) A set of programs which tells a computer how to perform its most basic tasks, such as "reading" information from input devices, "writing" information to output devices, launching application software, and executing the instructions of launched software. | (ref. 42) Also known as an "OS," this is the software that communicates with computer hardware on the most basic level. Without an operating system, no software programs can run. The OS is what allocates memory, processes tasks, accesses disks and peripherials, and serves as the user interface. | (photoref. 21 ) |
| Output devices | (ref. 43) Devices used by a computer to put out information. Common examples of output devices are monitors, printers, disc drives, and modems. (See, also,input devices.) | (ref. 44) Any device that outputs information from a computer is called, not surprisingly, an output device. Since most information from a computer is output in either a visual or auditory format, the most common output devices are the monitor and speakers. | (photoref. 22 ) |
| Peripheral | (ref. 45) Any hardware element which is peripheral to a computer's system unit. Common examples are input devices and output devices. Even output devices which are often found within the system unit, like disc drives and modems, are considered peripherals, because they are peripheral to the core elements of the computer: the CPU, RAM, and ROM. | (ref. 46) A computer peripheral is any external device that provides input and output for the computer. For example, a keyboard and mouse are input peripherals, while a monitor and printer are output peripherals. | (photoref. 23 ) |
| Primary storage | (ref. 47) A miniaturized electronic component which provides temporary storage of information. Primary storage is volatile and relatively expensive, but it's used because it is fast, and (with few exceptions) the only storage which the CPU can access directly. The single example of primary storage is RAM. | (ref. 48) Computer data storage, often called storage or memory, refers to computer components and recording media that retain digital data. Data storage is one of the core functions and fundamental components of computers. | (photoref. 24 ) |
| Programmable | (ref. 49) Capable of performing varied and different tasks, limited only by the sophistication of the programs provided. | (ref. 50) To provide (a machine) with a set of coded working instructions. | (photoref. 25 ) |
| Program | (ref. 51) A set of instructions which tells a computer what to do and when to do it. The instructions must be written in a language which the computer understands. | (ref. 52)An organized list of instructions that, when executed, causes the computer to behave in a predetermined manner. Without programs, computers are useless. | (photoref. 26 ) |
| RAM | (ref. 53) Random-Access Memory. See primary storage. | (ref. 54) a computer memory on which data can be both read and written and on which the location of data does not affect the speed of its retrieval; especially : RAM that acts as the main storage available to the user for programs and data ¡ªcalled also random-access memory | (photoref. 27 ) |
| ROM | (ref. 55) Read-Only Memory. A miniaturized electronic component which provides permanent storage of information. In most cases, the information in ROM is "written" only once, at the factory. Thereafter, ROM can be used only to read from, and not to write to. | (ref. 56)Memory hardware that allows fast access to permanently stored data but prevents addition to or modification of the data. | (photoref. 28 ) |
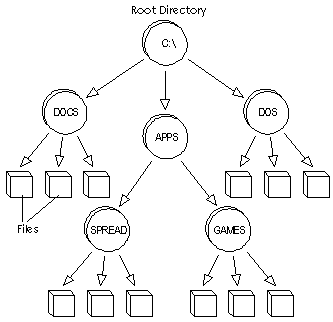
| Root | (ref. 57) Short for root directory the main directory, in a hierarchical directory structure, which (logically) contains all other directories. In DOS- andWindows-based systems, the root directory is represented by a backslash (\). In Mac OS, Unix, and Linux systems, the root directory is represented by a forward slash (/). | (ref. 58)he root folder of any partition is the "highest" folder in the hierarchy. The root folder contains all other folders and can also contain files. | (photoref. 29)  |
| Secondary storage | (ref. 59) Any storage medium which provides (relatively) permanent storage of information. Secondary storage is non-volatile and relatively inexpensive, but it¡¯s slow. With few exceptions, secondary storage cannot be accessed directly by the CPU. The most common examples of secondary storage are magnetic and optical discs and magnetic tape. | (ref. 60) Secondary storage technology refers to storage devices and storage media that are not always directly accessible by a computer. This differs from primary storage technology, such as an internal hard drive, which is constantly available. | (photoref. 30 ) |
| Software | (ref. 61) Synonym of program. | (ref. 62) Software is a general term for the various kinds of programs used to operate computers and related devices. (The term hardware describes the physical aspects of computers and related devices.) | (photoref. 31 ) |
| String | (ref. 63) A collection of like units, treated as a whole. For example, a string of characters, a string of bits. | (ref. 64) A string is a data type used in programming, such as an integer and floating point unit, but is used to represent text rather than numbers. It is comprised of a set of characters that can also contain spaces and numbers. | (photoref. 32 ) |
| System unit | (ref. 65) A plastic or metal box which contains the principal parts of a computer: the CPU, RAM, ROM, various connecting cables, and an AC/DC converter. In modern microcomputers, it's common to find peripheral devices installed inside the system unit; examples include disc drives and modems. | (ref. 66) A computer case (also known as a computer chassis, cabinet, box, tower, enclosure, housing, system unit or simply case) is the enclosure that contains most of the components of a computer (usually excluding the display, keyboard and mouse) | (photoref. 33 ) |
| USB | (ref. 67) Universal Serial Bus; a standard for connecting peripherals to a computer over inexpensive cables. | (ref. 68)(Universal Serial Bus) The most widely used hardware interface for attaching peripherals to a computer. There are typically at least two USB ports on laptops and four on desktop computers, while USB "hubs" allow many more connections. | (photoref. 34 ) |
To return to the index click HERE