BASIC COMPUTER GLOSSARY
| Words |
Class Definition |
Alternate Definition |
Image |
| Application Software |
A program which allows us to apply ourselves to a particular task, such as editing an image, accessing Internet resources, or playing a game. |
A program or group of programs designed for end users. Application software can be divided into two general classes: systems software and applications software. Systems software consists of low-level programs that interact with the computer at a very basic level. This includes operating systems, compilers, and utilities for managing computer resources.(Quinstreet inc. (2011a) |
 Wikipedia.org(2011) Wikipedia.org(2011) |
| ASCII |
American Standard Code for Information Interchange; an international standard for encoding characters into 7-bit codes. ASCII is the basis of the more modern Unicode standard. |
Acronym for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Pronounced ask-ee, ASCII is a code for representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127. For example, the ASCII code for uppercase M is 77. Most computers use ASCII codes to represent text, which makes it possible to transfer data from one computer to another.Quinstreet inc. (2011b) |
 Deciphering the Genetic Code(2011) Deciphering the Genetic Code(2011) |
| Binary Code |
A scheme for encoding data which uses only the digits 0 and 1. Binary code can be used to encode text, images, sounds, and programs, amongst other data. |
Code used in digital computers, based on a binary number system in which there are only two possible states, off and on, usually symbolized by 0 and 1.Farlex, Inc.(2011) |
 Desertlearning.com(2011) Desertlearning.com(2011) |
| Bit |
Contraction of the term “binary digit”; hence, either 0 or 1. |
Short for binary digit, the smallest unit of information on a machine. The term was first used in 1946 by John Tukey, a leading statistician and adviser to five presidents. A single bit can hold only one of two values: 0 or 1. More meaningful information is obtained by combining consecutive bits into larger units. For example, a byte is composed of 8 consecutive bits.Quinstreet inc. (2011c) |
 Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology(2011) Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology(2011) |
| Booting |
The process by which a computer loads its operating system into primary storage, from secondary storage, using the instructions found in ROM. |
"Start up a computer," 1975, from bootstrap (n.), 1953, "fixed sequence of instructions to load the operating system of a computer," on notion of the first-loaded program pulling itself, and the rest, up by the bootstraps.Douglas Harper (2011) |
 Ziff Davis, Inc.(2011) Ziff Davis, Inc.(2011) |
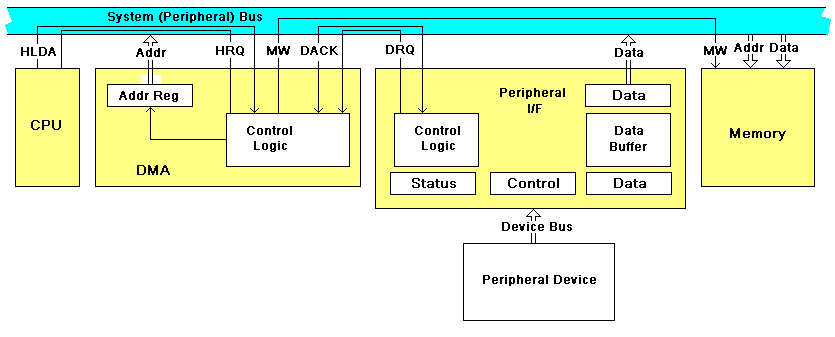
| Bus |
An electrical connection through which data are transmitted. |
A collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another. You can think of a bus as a highway on which data travels within a computer. When used in reference to personal computers, the term bus usually refers to internal bus. This is a bus that connects all the internal computer components to the CPU and main memory. There's also an expansion bus that enables expansion boards to access the CPU and memory.Quinstreet (2011d) |
 J.H.Young (2005) J.H.Young (2005) |
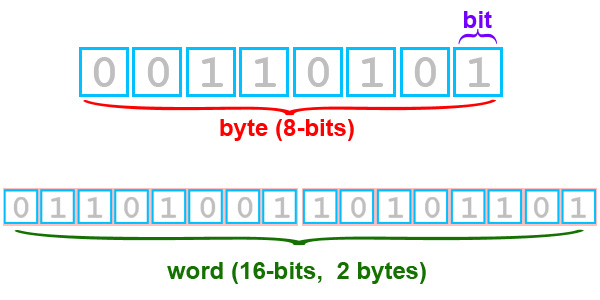
| Byte |
Contraction of the term “binary term”; the smallest unit of information which can be accessed directly by a computer. Most modern microcomputers use 8-bit, 16-bit, or 32 bit bytes. |
A component in the machine data hierarchy usually larger than a bit and smaller than a word;now most often eight bits and the smallest addressable unit of storage. A byte typically holds one characterComputer-dictionary-online.org(2011). |
 Bit Type Basics(2010) Bit Type Basics(2010) |
| Character |
A single letter or digit, or a special symbol like punctuation marks, the dollar sign, and a blank space. |
A device that computes, especially a programmable electronic machine that performs high-speed mathematical or logical operations or that assembles, stores, correlates, or otherwise processes information.QuinStreet Inc (2011e) |
 Cs.csubak.com(1998) Cs.csubak.com(1998) |
| Computer |
A programmable electronic device used for the processing of information |
A computer is an electronic machine that: takes in data and instructions (input), works with the data (processing) and puts out information (output)Tekmom.com/buzzwords (2011) |
 Robin Chung(2011) Robin Chung(2011) |
| CPU |
Central Processing Unit; a miniaturized electronic component which controls the execution of a computer and which performs basic arithmetic and logical operations. Colloquially called the computer’s “brain.” |
Pronounced as separate letters it is the abbreviation for central processing unit. The CPU is the brains of the computer. Sometimes referred to simply as the central processor, but more commonly called processor, the CPU is where most calculations take place. In terms of computing power, the CPU is the most important element of a computer system.QuinStreet Inc(2011j) |
 Eurotech (2011) Eurotech (2011) |
| Directory |
A logical collection of files, stored under a single name. |
An organizational unit, or container, used to organize folders and files into a hierarchical structure. Directories contain bookkeeping information about files that are, figuratively speaking, beneath them in the hierarchy. You can think of a directory as a file cabinet that contains folders that contain files. Many graphical user interfaces use the term folder instead of directory.QuinStreet Inc(2011k) |
 Nickhill.com(2011) Nickhill.com(2011) |
| File |
A logical collection of information, stored under a single name. |
A collection of related data or program records stored on some input/output or auxiliary storage medium.Houghton Mifflin (2002a) |
 Top-Windows-Tutorial.com (2011) Top-Windows-Tutorial.com (2011) |
| Firewire |
Applies name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus, also called iLink by Sony and Lynx by Texas Instruments. |
"FireWire", "I-Link") A 1995 Macintosh/IBM PC serial bus interface standard offering high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data services. 1394 can transfer data between a computer and its peripherals at 100, 200, or 400 Mbps, with a planed increase to 2 Gbps. Cable length is limited to 4.5 m but up to 16 cables can be daisy-chained yielding a total length of 72 mDenis Howe (2011a). |
 KBS, Inc. (2010) KBS, Inc. (2010) |
| Gigabyte |
230 bytes; approximately 1 billion bytes. |
A gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power, or 1,073,741,824 bytes. Techterms.com(2008) |
 Amazon.com, Inc (2011) Amazon.com, Inc (2011) |
| Hardware |
The physical parts of the computer; any part of the computer which can be seen and touched. (cf. software.) |
Computer hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer and related devices. Internal hardware devices include motherboards, hard drives, and RAM. External hardware devices include monitors, keyboards, mice, printers, and scanners. Techterms.com(2008) |
 Warepin (2010) Warepin (2010) |
| Information |
Words, pictures, and sounds which have meaning to us. |
Information is stimuli that has meaning in some context for its receiver. When information is entered into and stored in a computer, it is generally referred to as data. After processing (such as formatting and printing), output data can again be perceived as information. When information is packaged or used for understanding or doing something, it is known as knowledge. TechTarget (2011) |
 Buzzle.com(2011) Buzzle.com(2011) |
| Input devices |
Devices used to put information into a computer. Common examples of input devices are keyboards, mouses, disc drives, and modems. (See, also, output devices.) |
A peripheral used to transfer data from the outside world into a computer system. Some input devices are operated directly by the user, e.g. keyboard, mouse, touch screen, joystick, digitising tablet, microphone; others are sensors or transducers which convert external signals into data, e.g. using an ananlog to digital converter (this would also be true of a microphone). Other kinds of inputs are really one half of a bidirectional link with another computer or storage device, e.g. serial line, SCSI interface. Denis Howe (2010b) |
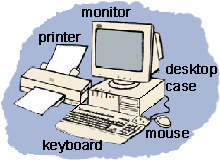 Ollnet.com(2011) Ollnet.com(2011) |
| Kilobyte |
210 bytes; approximately 1 thousand bytes. |
1024 bytes;2120. Merriam-Webster, Incorporated (2011) |
 Liyana (2010) Liyana (2010) |
| Megabyte |
2 20 bytes; approximately 1 million bytes. |
When used to describe data storage, 1,048,576 (2 to the 20th power) bytes. Megabyte is frequently abbreviated as M or MB. QuinStreet Inc (2011f) |
 Desertlearning.com(2011) Desertlearning.com(2011) |
| Monitor |
A visual-display device, on which a computer displays information about its internal state, allowing people to monitor the activities of the computer. |
A cathode-ray tube and associated electronics connected to a computer's video output. A monitor may be either monochrome (black and white) or colour (RGB). Colour monitors may show either digital colour (each of the red, green and blue signals may be either on or off, giving eight possible colours: black, white, red, green, blue, cyan, magenta and yellow) or analog colour (red, green and blue signals are continuously variable allowing any combination to be displayed). Digital monitors are sometimes known as TTL because the voltages on the red, green and blue inputs are compatible with TTL logic chips. enis Howe (2010c) |
 YouKong Inc.(2009) YouKong Inc.(2009) |
| Operating System |
A set of programs which tells a computer how to perform its most basic tasks, such as “reading” information from input devices, “writing” information to output devices, launching application software, and executing the instructions of launched software. |
(OS) The low-level software which handles the interface to peripheral hardware, schedules tasks, allocates storage, and presents a default interface to the user when no application program is running.Denis Howe (2010d) |
 WordPress.(2011) WordPress.(2011) |
| Output Devices |
Devices used by a computer to put out information. Common examples of output devices are monitors, printers, disc drives, and modems. (See, also, input devices.) |
Electronic or electromechanical equipment connected to a computer and used to transfer data out of the computer in the form of text, images, sounds or other media to a display screen, printer, loudspeaker or storage device. Most modern storage devices such as disk drives and magnetic tape drives act as both input and output devices, others such as CD-ROM are input only.Denis Howe (2010e) |
 Sabrez Alam (2011) Sabrez Alam (2011) |
| Peripheral |
Any hardware element which is peripheral to a computer’s system unit. Common examples are input devices and output devices. Even output devices which are often found within the system unit, like disc drives and modems, are considered peripherals, because they are peripheral to the core elements of the computer: the CPU, RAM, and ROM. |
An auxiliary device, such as a printer or modem, distinct from a computer's central processing unit and working memory, and often connected externally. Houghton Mifflin (2002b) |
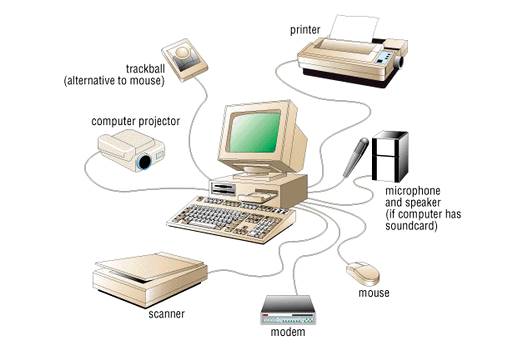 Tiscali UK Limited trading as TalkTalk (2011) Tiscali UK Limited trading as TalkTalk (2011) |
| Primary Storage |
A miniaturized electronic component which provides temporary storage of information. Primary storage is volatile and relatively expensive, but it’s used because it is fast, and (with few exceptions) the only storage which the CPU can access directly. The single example of primary storage is RAM. |
A somewhat dated term for main memory. Mass storage devices, such as disk drives and tapes, are sometimes called secondary storage.QuinStreet Inc (2011g) |
 CompuInfoSystems(2011) CompuInfoSystems(2011) |
| Programmable |
Capable of performing varied and different tasks, limited only by the sophistication of the programs provided. |
An electronic device, as a calculator or telephone, that can be programmed to perform specific tasks. Houghton Mifflin (2002c) |
 All Products Online Corp.(2011) All Products Online Corp.(2011) |
| Program |
A set of instructions which tells a computer what to do and when to do it. The instructions must be written in a language which the computer understands. |
Program is a common computer term that can be used as both a noun and a verb. A program (noun) is executable software that runs on a computer. It is similar to a script, but is often much larger in size and does not require a scripting engine to run. Instead, a program consists of compiled code that can run directly from the computer's operating system.Techterms.com(2008) |
 Wordpress.com (2011) Wordpress.com (2011) |
| RAM |
Random-Access Memory. See primary storage. |
(RAM) (Previously "direct-access memory"). A data storage device for which the order of access to different locations does not affect the speed of access. This is in contrast to, say, a magnetic disk, magnetic tape or a mercury delay line where it is very much quicker to access data sequentially because accessing a non-sequential location requires physical movement of the storage medium rather than just electronic switching.Denis Howe (2010f) |
 Cspitt.com(2007) Cspitt.com(2007) |
| ROM |
Read-Only Memory. A miniaturized electronic component which provides permanent storage of information. In most cases, the information in ROM is “written” only once, at the factory. Thereafter, ROM can be used only to read from, and not to write to. |
Read Only Memory (ROM) is computer memory that can permanently store data and applications within itAbout.com (2011b). |
 Awesome Inc.(2011) Awesome Inc.(2011) |
| Root |
Short for “root directory” the main directory, in a hierarchical directory structure, which (logically) contains all other directories. In DOS- and Windows-based systems, the root directory is represented by a backslash (\). In Mac OS, Unix, and Linux systems, the root directory is represented by a forward slash (/). |
The top directory in a file system. The root directory is provided by the operating system and has a special name; for example, in DOS systems the root directory is called \. The root directory is sometimes referred to simply as the root. QuinStreet Inc(2011h) |
 Club.myce.com(2006) Club.myce.com(2006) |
| Secondary Storage |
Any storage medium which provides (relatively) permanent storage of information. Secondary storage is non-volatile and relatively inexpensive, but it’s slow. With few exceptions, secondary storage cannot be accessed directly by the CPU. The most common examples of secondary storage are magnetic and optical discs and magnetic tape. |
Secondary storage technology refers to storage devices and storage media that are not always directly accessible by a computer. This differs from primary storage technology, such as an internal hard drive, which is constantly available. Techterms.com(2009) |
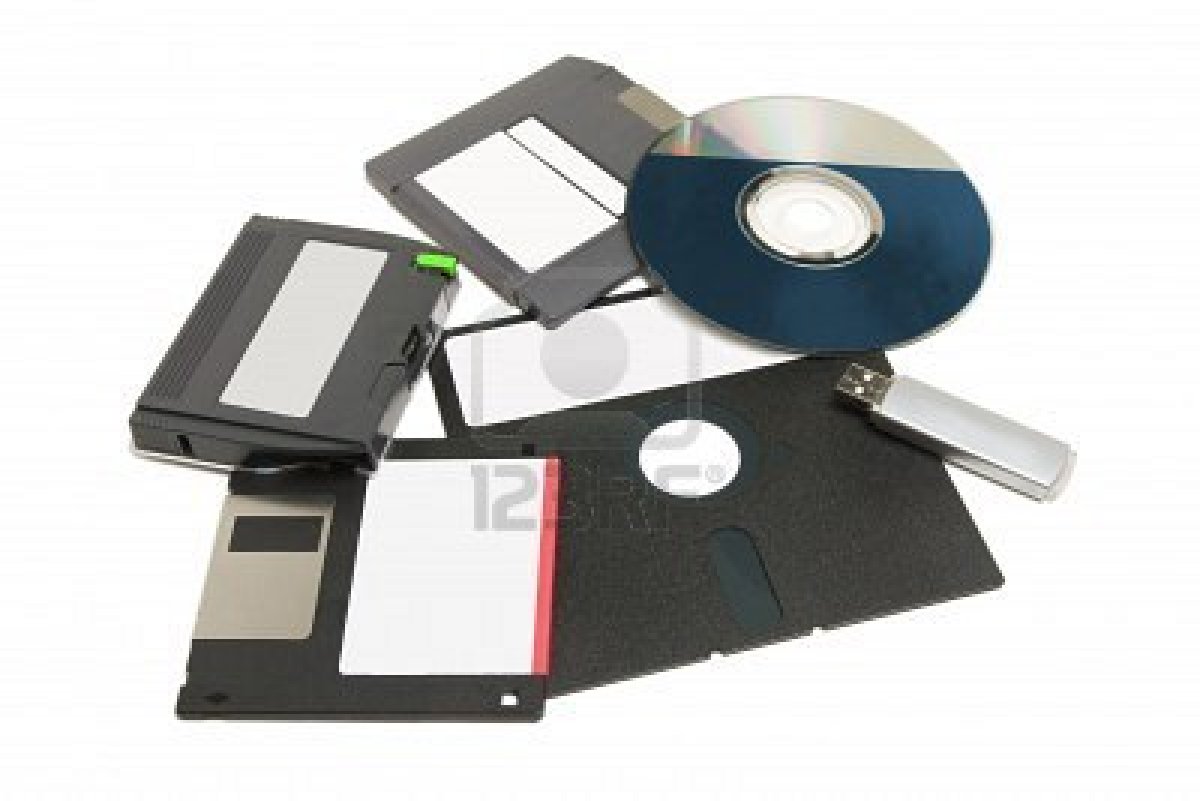 123RF Limited (2011) 123RF Limited (2011) |
| Software |
Synonym of program. |
The programs, programming languages, and data that direct the operations of a computer system. word processing programs and Internet browsers are examples of software. Houghton Mifflin (2002d) |
 Softdistrict (2010) Softdistrict (2010) |
| String |
A collection of like units, treated as a whole. For example, a string of characters, a string of bits. |
A series of characters manipulated as a group. A character string differs from a name in that it does not represent anything -- a name stands for some other object.QuinStreet Inc(2011i) |
 Cspitt.com(2007) Cspitt.com(2007) |
| System Unit |
A plastic or metal box which contains the principal parts of a computer: the CPU, RAM, ROM, various connecting cables, and an AC/DC convertor. In modern microcomputers, it’s common to find peripheral devices installed inside the system unit; examples include disk drives and modems. |
This is the technical term that refers to the box that houses your computer. The system unit refers to the computer itself but does not include the monitor, the keyboard, the mouse, or any other peripherals. I suppose most people will probably know what you mean when you refer to "the box," but saying "system unit" will definitely make you sound more sophisticated. iWEBTOOL inc. (2008) |
 Alan Simpson (2011) Alan Simpson (2011) |
| USB |
Universal Serial Bus; a standard for connecting peripherals to a computer over inexpensive cables. |
(Universal Serial Bus) The most widely used hardware interface for attaching peripherals to a computerAbout.com (2011a). |
 KeyGhost Ltd (2000) KeyGhost Ltd (2000) |
Back to homepage
 Wikipedia.org(2011)
Wikipedia.org(2011) Deciphering the Genetic Code(2011)
Deciphering the Genetic Code(2011) Desertlearning.com(2011)
Desertlearning.com(2011) Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology(2011)
Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology(2011) Ziff Davis, Inc.(2011)
Ziff Davis, Inc.(2011)  J.H.Young (2005)
J.H.Young (2005) Bit Type Basics(2010)
Bit Type Basics(2010) Cs.csubak.com(1998)
Cs.csubak.com(1998) Robin Chung(2011)
Robin Chung(2011) Eurotech (2011)
Eurotech (2011)  Nickhill.com(2011)
Nickhill.com(2011) Top-Windows-Tutorial.com (2011)
Top-Windows-Tutorial.com (2011)  KBS, Inc. (2010)
KBS, Inc. (2010) Amazon.com, Inc (2011)
Amazon.com, Inc (2011) Warepin (2010)
Warepin (2010) Buzzle.com(2011)
Buzzle.com(2011)  Ollnet.com(2011)
Ollnet.com(2011)  Liyana (2010)
Liyana (2010) Desertlearning.com(2011)
Desertlearning.com(2011)  YouKong Inc.(2009)
YouKong Inc.(2009) WordPress.(2011)
WordPress.(2011) Sabrez Alam (2011)
Sabrez Alam (2011) Tiscali UK Limited trading as TalkTalk (2011)
Tiscali UK Limited trading as TalkTalk (2011) CompuInfoSystems(2011)
CompuInfoSystems(2011)  All Products Online Corp.(2011)
All Products Online Corp.(2011) Wordpress.com (2011)
Wordpress.com (2011) Cspitt.com(2007)
Cspitt.com(2007) Awesome Inc.(2011)
Awesome Inc.(2011)  Club.myce.com(2006)
Club.myce.com(2006) 123RF Limited (2011)
123RF Limited (2011)  Softdistrict (2010)
Softdistrict (2010) Cspitt.com(2007)
Cspitt.com(2007)  Alan Simpson (2011)
Alan Simpson (2011)  KeyGhost Ltd (2000)
KeyGhost Ltd (2000)