| Terms |
Class Definition |
Web Definition |
Pictures |
| application software |
A program which allows us to apply ourselves to a particular task, such as editing an image, accessing Internet resources, or playing a game |
Application software is a subclass of computer software that employs the capabilities of a computer directly and thoroughly to a task that the user wishes to perform
(Science Daily, 1995- 2010). |

Application software diagram and examples |
| ASCII |
American Standard Code for Information Interchange; an international standard for encoding characters intp 7-bit codes; ASCII is the basis of the more modern and inclusive Unicode standar |
Acronym for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. Pronounced ask-ee, ASCII is a code for representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127
(Webopedia, 2011). |

A portion/example of some ASCII codes |
| binary code |
A scheme for encoding data using only digits 0 and 1; binary code can be used to encode text, images, sounds, and programs, amongst other data |
Computers use a special code of their own to express the digital information they process. It's called the binary code because it consists of only two symbols- 0s and 1s
(Intel, 2011). |

Binary codes of some ASCII characters, letters, and digits |
| bit |
Contraction of the term binary digit; hence 0 or 1 |
A fundamental unit of information having just two possible values, as either of the binary digits 0 or 1
(Answers.com. 2011). |
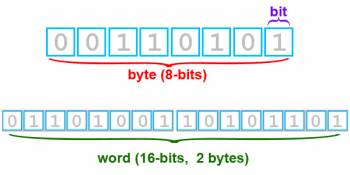
Example of a binary digit (bit) |
| booting |
The process by which a computer loads its operating system in primary storage from secondary storage using the instructions found in ROM |
To boot (as a verb; also "to boot up") a computer is to load an operating system into the computer's main memory or random access memory (RAM)
(Searchwinit.com, 2000). |
Screenshot of a computer booting |
| bus |
An electrical connection through which data are transmitted. Different buses may go by different names. |
In a computer or on a network, a bus is a transmission path on which signals are dropped off or picked up at every device attached to the line. Only devices addressed by the signals pay attention to them; the others discard the signals
(Searchstorage.com, 1998). |

A computer bus, taken out and displayed |
| byte |
Contraction of the term binary term; the smallest unit of information which can be accessed directly by a computer. Most modern computers use 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit or 64-bt bytes. |
Adjacent bits, usually eight, processed by a computer as a unit; the combination of bits used to represent a particular letter, number, or special character
(Dictionary.com, 2011). |

Example of a binary digit (bit) |
| character |
A single letter or digit, or a special symbol like punctuation marks, the dollar sign, and a blank space |
Any letter, numeral, etc, which is a unit of information and can be represented uniquely by a binary pattern
(Dictionary.com, 2011). |

Section of Character Map |
| computer |
A programmable electronic device for the processing of information |
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or "data." It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data
(GCFLearnFree.org, 1998- 2011). |

Image of a desktop computer |
| CPU |
Central Processing Unit; a miniaturized electronic component which controls the execution of a computer and which performs basic arithmetic and logical operations. Colloquially called the computer's brain. |
Also known as the Central Processing Unit or processor, the CPU is essentially the "brains" of your computer
(Dana Hinders, 2003- 2011). |

A single board computer CPU |
| directory |
A logical collection of files stored under a single name |
A directory is a named group of related files that are separated by the naming convention from other groups of files
(Searchwinit.com, 1998). |

An example of a directory (shown as folders) |
| file |
A logical collection of data stored under a single name |
A collection of related data or program records stored as a unit with a single name
(Answers.com, 2011). |

An example of highlighted files in a directory |
| FireWire |
Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus, also called iLiINK by Sony and Lynx by Texas Instruments |
FireWire is a method of transferring information between digital devices, especially audio and video equipment. Also known as IEEE 1394
(Jeff Tyson & Julia Layton, 1998- 2011). |

A FireWire connecter opening |
| gigabyte |
2^30 bytes (approximately 1 billion bytes) |
A measure of computer data storage capacity and is "roughly" a billion bytes. A gigabyte is two to the 30th power
(Searchstorage.com, 2000- 2011). |

Screenshot of a conversion from gigabyte to byte |
| hardware |
The physical parts of the computer; any part of the computer which can be seen or touched |
Refers to objects that you can actually touch, like disks, disk drives, display screens, keyboards, printers, boards, and chips
(Webopedia, 2011). |

A diagram of basic hardware to be found |
| information |
Words, pictures and sounds which have meaning to us |
The meaning given to data by the way in which it is interpreted
(Dictionary.com, 2011). |

Basic points of logical information |
| input devices |
Devices used to put in information into a computer. Common examples of input devices are keybaords, scanners, game controllers, USB drives, motion sensors and modems. |
An input device is any hardware device that sends data to the computer, without any input devices, a computer would only be a display device and not allow users to interact with it, much like a TV
(Computerhope.com, 2011). |

Keyboard and mouses are examples of input devices |
| kilobyte |
2^10 bytes (approximately 1 thousand bytes) |
A kilobyte is 1024 bytes
(Malektips.com, 1997- 2011). |

A printscreen of a conversion from kilobytes to bytes |
| megabyte |
2^20 bytes (approximately 1 million bytes) |
A megabyte is 1,048,576 bytes
(Dictionary.com, 2011). |

A printscreen of a conversion from megabytes to bytes |
| monitor |
A visual-display device, on which a computer displays information, about its internal state, allowing people to monitor the activities of the computer |
Another term for display screen. The term monitor, however, usually refers to the entire box, whereas display screen can mean just the screen
(Webopedia, 2011). |

A desktop monitor |
| operating system |
A set of programs which tells a computer how to perform its most basic tasks, wush as "reading" information from input devices, "writing" information to output devices, and executing the instructions of launched software |
The most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs
(Webopedia, 2011). |
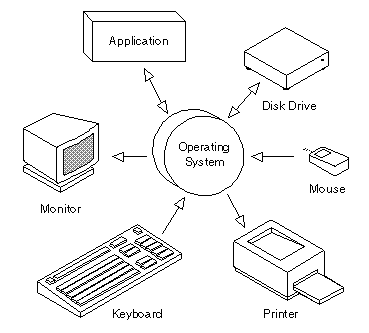
Components that make up an operating system |
| output devices |
Devices used to put in information into a computer to put out information. Common examples of output devices are monitors, speakers, and data modems. |
Any machine capable of representing information from a computer. This includes display screens, printers, plotters, and synthesizers
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Examples of output devices |
| peripheral |
Any hardware element which is peripheral to a computer's system unit. Common examples are input devices and output devices. Even output devices which are often found within the system unit like modems and disc drives are considered peripherals, because they are peripheral to the core elements of the computer:CPU, RAM, and ROM. |
A computer device, such as a CD-ROM drive or printer, that is not part of the essential computer, i.e., the memory and microprocessor
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Examples of a peripheral device inside the system unit |
| primary storage |
A miniaturized electronic component which provides temporary storage of information. Primary storage is volatile and relatively expensive, but it's used because it's fast and (with few exceptions) is the only storage which the CPU can access directly (RAM). |
Primary storage, also known as main storage or memory, is the main area in a computer in which data is stored for quick access by the computer's processor
(Searchstorage.com, 1998). |

Diagram of primary storage in relation to other storages |
| programmable |
Capable of performing varied and different tasks, limited only by the sophistication of the programs provided |
An electronic device, as a calculator or telephone, that can be programmed to perform specific tasks
(Dictionary.com, 2011). |

Example of a programmable product |
| program |
A set of instructions which tells a computer what to do and when to do it; the instructions must be written in a language which the computer understands |
An organized list of instructions that, when executed, causes the computer to behave in a predetermined manner. Without programs, computers are useless
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Examples of computer programs |
| RAM |
Random Access Memory; because you can access it in random order |
Acronym for random access memory, a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly; that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Random Acess Memory |
| ROM |
Read Only Memory; contains just enough information for the computer to read the first bit of the operating system |
Acronym for read-only memory, computer memory on which data has been prerecorded
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Read Only Memory |
| root |
Short for "root directory"; the main directory, in a hierarchical directory structure, which (logically) contains all other directories; in Dos-and Windows- based ssyteems, the root directory is represented by a backslash(\); in Mac OS, Unix, and Linux systems, the root directory is represented by a slash(/) |
In computer file system, the root (root directory) is the first or top-most directory in a hierarchy. It can be linked to the root of a tree- the starting point where all branches originate
(Wikipedia, 2011). |

A branching of the root directory |
| secondary storage |
Any storage medium which provides (relatively) permanent storage of information. Secondary storage is novolatile and relatively inexpensive, but it's slow. With few exceptions, secondary storage cannot be accessed directly by the CPU. The most common examples of secondary storage are the magnetic and optical discs, magnetic tape, and flash memory. |
Secondary storage (or secondary memory) is the slowest and cheapest form of memory. It cannot be processed directly by the CPU. It must first be copied into primary storage (also known as RAM )
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Examples of secondary storage devices |
| software |
A synonym of program |
Computer instructions or data; anything that can be stored electronically is software. The storage devices and display devices are hardware
(Webopedia, 2011). |

Examples of common computer softwares |
| string |
A collection of like units, treated as a whole; Examples: character string, or bit string |
A string is a data type used in programming, such as an integer and floating point unit, but is used to represent text rather than numbers
(iwebtool.com, 2005- 2008). |

Table of bit string samples |
| system unit |
A plastic or metal box which contains the principal parts of a computer: the CPU, RAM, ROM, various connecting cables and an AC/DC converter. In modern microcomputers, it's common to find peripheral devices installed inside the system unit; Examples include: modems and card readers. |
The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard or monitor, or any peripheral devices
(Webopedia, 2011). |

A simple drawing of the system unit |
| USB |
Universal serial bus; a standard for connecting peripherals to a computer over inexpensive cables |
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices
(Wikipedia, 2011). |

Examples of USBs |

































